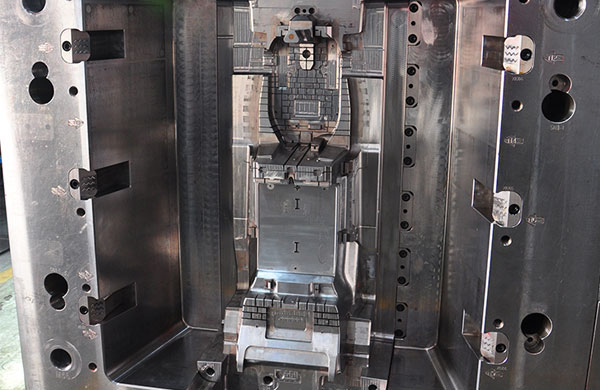
About laptop shell plastic injection mold
Why choose injection molding?
Injection molding can handle extremely complex parts, and uniformity, as well as the ability to make millions of virtually identical parts. To optimize the effectiveness of high-volume injection molding and maximize the precision and quality of your parts, key design elements should be taken into account.
What is the difference between 3D printing and injection moulding?
3D printing
3D printing is additive manufacturing, which means the initial material is built layer by layer. 3D printing creates three-dimensional objects from reading a virtual computer design and reproduces it into a tangible part by using material filaments or powders.
Injection moulding
Injection moulding makes use of moulds. First, an object’s inverse is machined out of a material (e.g. aluminium, tool steel) that is safe to handle the molten build material (the material the finished object is made of). Then, the molten build material is poured into the mould. Once the material has cooled in the mould, the part is ready.
Parts manufactured through injection moulding consist of a single poured layer, which adds strength to the shape because there are no fissures or points of weakness. Whereas in 3D printing, the part is made layer by layer which impacts its overall strength. 3D printing can create visible ridges and structural faults during manufacturing that typically don’t occur with plastic injection moulding.